Preparation of Low Molecular Weight Glucomannan from A. Konjac K. Koch in Vietnam by Enzyme Catalyzed Hydrolysis Reaction and its Prospective use to Lower Blood Sugar Levels-Juniper Publishers
JUNIPER PUBLISHERS- ACADEMIC JOURNAL OF POLYMER
SCIENCE

Abstract
In order to break down the glycoside bond in
glucomannan obtained from the bulb of the Konjac in Việt Nam, we used
the extract from bacteria bacillus subtilis. The reaction was carried
out at 40oC for 6h, pH 5 and the E/S ratio of 0.4(w/w). The obtained
oligo-glucomannan after hydrolysis that had molecular weight lower than
1748Da was tested for glucose tolerence in experimental animals. The
test results showed that the hydrolyzed glucomannan at a dose of 6g/kg
was more effective in lowering blood glucomannan in mouse models that
were made to have blood sugar increase exogenously by oral admistration,
as compared to original glucomannan.
Keywords: Hydrolyzed glucomannan; Enzyme; Blood sugar
Introduction
Glucomannan is a water-soluble polysaccharide
consisting of D-mannose and D-glucose units linked with β - (1→ 4)
glucosidic bonds, with the degree of branching of about 8% via β-1,3- or
β-1,6-glucosidic linkages and the degree of acetylation of 5÷10%. Being
a soluble fiber, low in energy, that acts as a sweeper to prevent
cholesterol absorption into the bloodstream, glucomannan is used to lose
weight, reduce blood cholesterol, blood fat and blood sugar with very
few side effects [1,2].
Despite its hydrophilicity, glucomannan is poorly
soluble in water (solubility of around 30%) due to its high molecular
weight, which limits its application range in certain areas [3]. In
order to increase its solubility, glucomannan is hydrolyzed to lower its
molecular weigh and the process attracts the attention of many
scientists. Studies on the methods of preparing low molecular weight
glucomannan have been of interest to many authors worldwide, including
enzymatic hydrolysis [4,5]. treatment with hydrochloric acid combined
with ultrasound [6], hydrolysis under the effect of gamma-ray combined
with ethanol [7], treatment with gamma-ray combined with H2O2 [8],
alkaline hydrolysis combined with heat [9]. With superior catalytic
activity compared to chemical catalysts and high biological safety,
enzymes have brought many great achievements in several fields such as
industry, agriculture, pharmaceutical chemistry, etc. As a result, the
exploitation and use of enzymes are being considered by many
countries in the world. The work by Wenjie Jian et al investigated the
Konjac glucomannan hydrolysis reaction with γ rays combined with
Endo-(1, 4)-mannanase enzymes, yielding a product with molecular weight
lower than 2200 Da [6].
Cheng YU Chen et al. [5] also carried out the
hydrolysis reaction of glucomannan with β mananase enzyme, lowering the
molécular weight to 3089 Da [10]. In this study, we conducted the
hydrolysis reaction of glucomannane obtained from the bulbs of Konjac
grown in Vietnam by the enzyme produced by the bacteria bacillus
substilis. The hydrolyzed product was tested for blood glucose tolerence
in experimental mice.
Experimental
Materials & chemicals
Purified glucomannan from A. KONJAC K. KOCH in
VIETNAM was prepared iou laboratory [11]. Enzyme endo-1,4 β-Mannanase
(Bacillus sp.) EC 3.2.1.78 CAZy Family: GH26 CAS: 37288-54-3 was from
Megazyme Company, all other chemicals were obtained from Merck, used
immediately without purification.
Research methods and equipment
Enzyme from bacteria Bacillus subtilis
Among amylase-producing microoraganisms, Bacillus
subtilis is a thermophilic bacterium able to grow rapidly (4-6 times
faster than moisturephilic bacteria) and grows well at relatively high
temperatures. Therefore, its culture is less likely to be infected by
other microoraganisms.
Bacillus subtilis belongs to: Order: Eubacteriales Family:
Bacillaceae Genus: Bacillus Species: Bacillus subtilis
It is an aerobic microorganism with optimum temperatures
for growth in the range from 36oC to 50oC, the maximum of about
60oC, the spores can resist relatively high heat. In the extract of
Bacillus subtilis there are various enzymes, including β-amylase,
cellulase, capable of hydrolyzing β - (1→ 4) glucosidic linkages in
glucomannan [12].
Hydrolysis of Glucomannan
The proper digestive environment for decomposing
polysaccharides is slightly acidic and the body temperature is
within the enzyme’s active temperature range. We carried out the
reaction as follows:
a) Weigh about 10g of substrate for each sample
b) Disperse glucomannan in 300ml H2O, adjust the solution
pH to 5 with HCl. Add 4ml enzyme extract to the solution.
Agitate the mixture to homogenous solution.
c) Incubate the mixture in a warm cabinet at 40oC for 24h.
d) At the end of the reaction, add excess absolute ethanol
to the mixture, centrifuge at 9000 rpm. Remove the liquid,
vacuum dry at 50oC to constant weight. The obtained product
was hydrolyzed glucomannan, named as LMWG-S.
Blood glucose tolerance of the product
The ability to stimulate blood glucose tolerence of the
hydrolyzed product was determined in normal, healthy mice by
oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT). The test mice were white mice
(of Swiss strains), both male and female, weighing 18-22 grams,
having healthy physiology.
The mice were fed daily with synthetic feed supplied by
the Institute of Vaccines and Biologicals. They were exposed to
light from 12am to 12pm. The mice were divided into test lots,
each with 10 individuals. After stable culture under laboratory
conditions, the mice were tested for blood glucose tolerence by
taking the following preparations:
a) Test lot 1 (control): distilled water.
b) Test lot 2: hydrolyzed glucomannan at a dose of 3g/kg
body weight.
c) Test lot 3: hydrolyzed glucomannan at a dose of 6g/kg
body weight.
d) Test lot 4: glucomannan at a dose of 6g/kg body weight.
e) Test lot 5: gliclazide at a dose of 10mg/kg body weight.
f) Just after the mice were given the preparations, the
blood glucose level was measured (0h).
g) After 2h the mice were fed with glucose at a dose of 2g/
kg body weight to increase blood glucose.
h) Measure blood glucose levels 2h, 2h30, 3h và 4h after
taking the preparations.
Results
(LMWG-S)
The obtained product after the hydrolysis reaction of
glucomannan was a translucent white, water soluble powdered
mass that could be finely ground. The yield reached 65%.
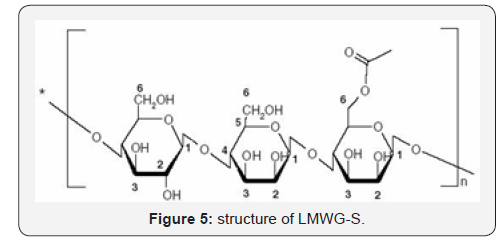
Structure and properties of LMWG-S
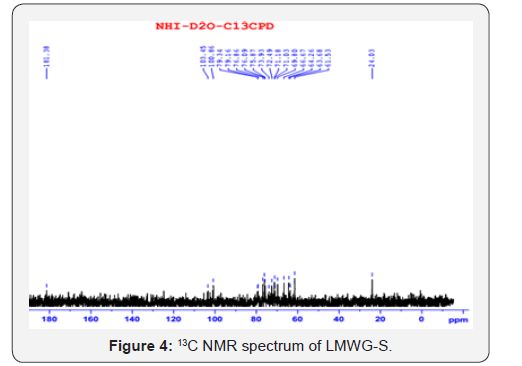
The spectra of IR, NMR, TGA of the product are shown in
(Figures 1-5).

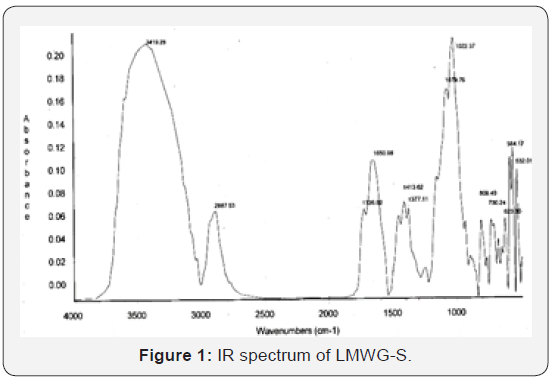
The typical peaks on the IR spectrum of the product (Figure
1) are inferred as follows: the area 3000-3700cm-1 represents
the covalent vibration of the hydroxyl group (-OH); 2887cm-
1 represents the covalent vibration of the CH linkage (υC–H);
1726cm-1 represents the covalent vibration of the carbonyl
group (υC=O); 1650cm-1 represents the presence of absorbed
water molecules; 1413 and 1377cm-1 represent the deformation
vibration of the CH linkage (CH); 1150cm-1 represents the
covalent vibration of the ether linkage C-O-C between units in
polysaccharide macromolecule; 1079 and 1022cm-1 represent
the covalent vibration of the C-O linkage of the C-OH group. The
peaks in the area 808÷900 cm-1 represents the α pyranose ring
of glucose and mannose. Thus, the chemical structure of the
hydrolyzed glucomannan is virtually unchanged from the original
glucomannan. This may result from the fact that the hydrolysis
reaction under the experimental conditions takes place mainly at
the 1-4 glycosidic linkage.
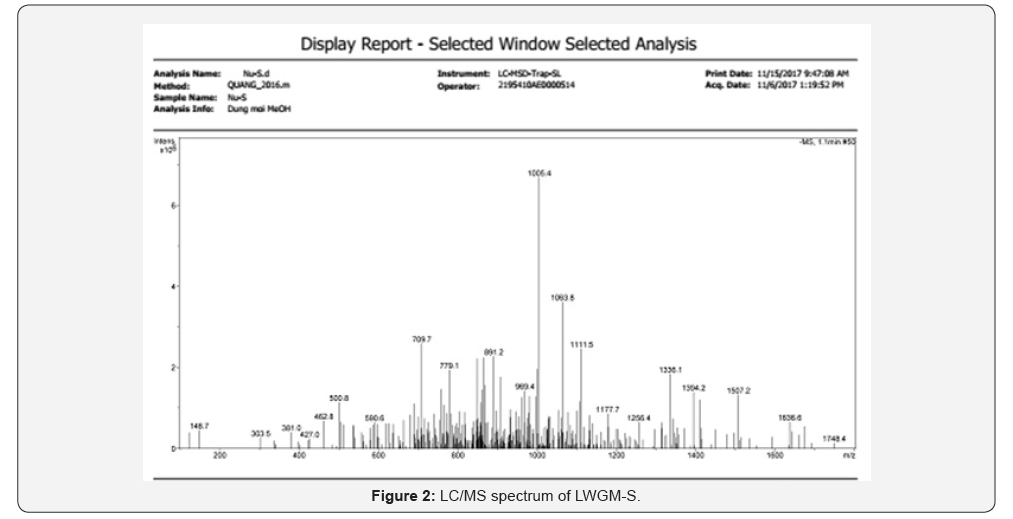
As shown in Figure 2, the hydrolyzed product mixture has
the maximum molecular weight of 1748.4Da. The molecular
weight of glucomannan is reduced to 1748,4Da, which proves the
effectiveness of the experimental model. The optimal conditions
for hydrolysis are similar to the results reported by Cheng YU Chen
et al. [13]. However, the hydrolysis process of our experimental
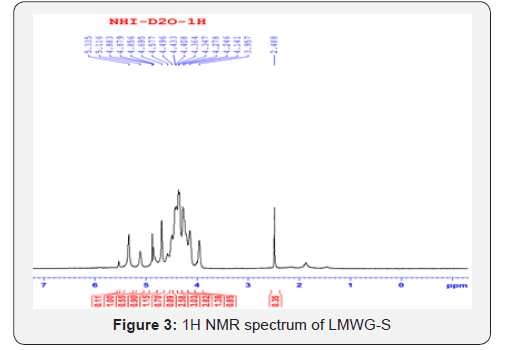
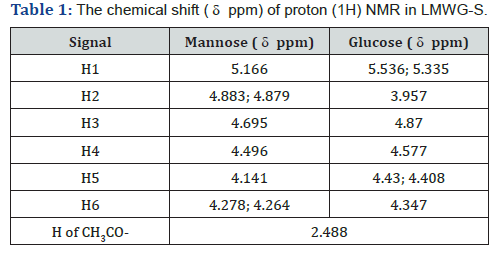
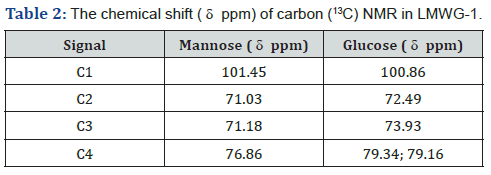
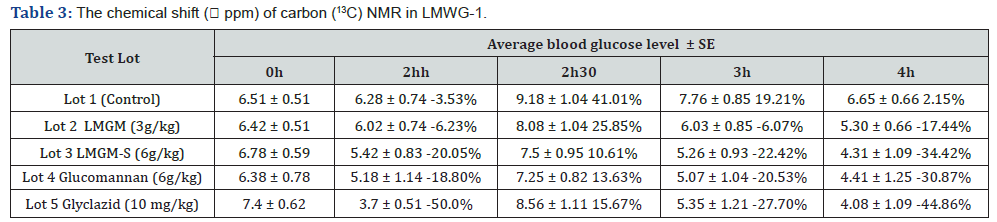
model results in oligo glucomannan with lower molecular weight.The chemical shift ( ppm) of 1H and (13C) in konjac glucomannan
molecules is shown in Tables 1 & 2, respectively [14-19].
The M/G ratio is calculated as follows: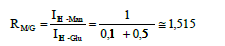
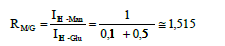
This result shows that the M/G ratio of the hydrolyzed product
is slightly lower than that of the original GM (RM/G 1.6) [3].




The result shows that DA of the hydrolyzed product is lower
than that of the original raw material, proving that together with
the hydrolysis reaction at the 1,4-β-D glycosidic linkage, de-Nacetylation
also occurred, which leads to DA decrease of the
product


Blood glucose tolerance of the product
The blood glucose tolerance test is an experimental
method
often used in recent studies in Vietnam and in the world. There are also
studies that attemp to test the inhibition of glucose absorption
in the intestine through food or glucose solution. However, this
study focuses on the cellular glucose tolerence, an important
indicator to assess the effects of diabetes medications. The effect
of the product on blood glucose tolerence is demonstrated by
changes in blood glucose level of mice after administration of
2mg/kg body weight. The research results are shown in the Table
3 below

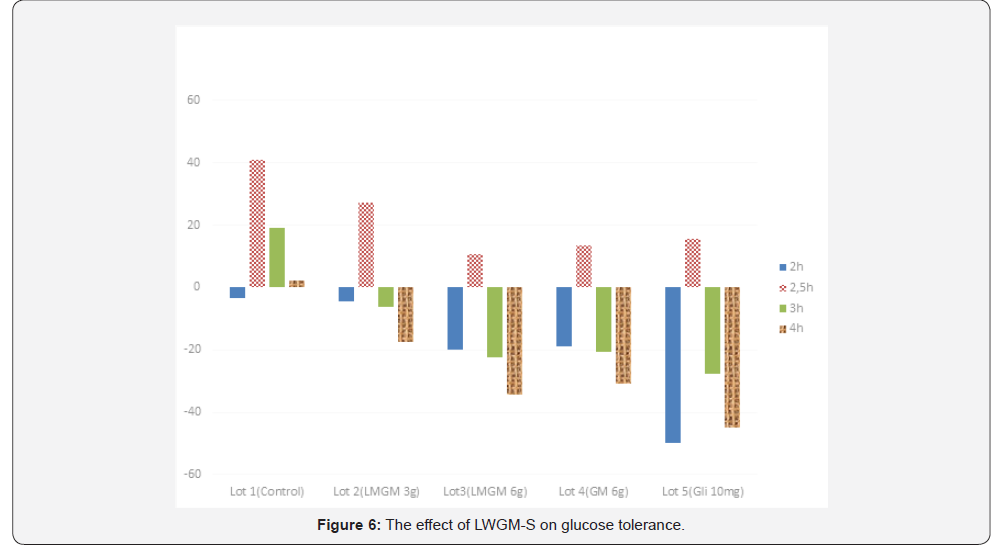
The results from Table 3 and Figure 6 show that at the time of
glucose feeding (2 hours after taking the preparations), all the test
lots had a reduced blood glucose level, due to fasting. At the time
2.5 hours after taking the preparations because the mice were
fed with glucose at a dose 2g/kg body weight, the blood glucose
level in all lots increased (and reached the maximum). This level
gradually decreased at the time 3 and 4 hours after glucose
feeding. At the time 2.5 hours after the feeding, lots number 2, 3,
4 and 5 had lower blood glucose increase than lot 1 (as control),
the difference is statistically significant (P≤ 0,05). Three and four
hours after taking the preparations, lots number 2, 3, 4 and 5
had greater blood glucose reduction than lot 1. The difference is
statistically insignificant (P>0,05) on the blood glucose reduction
percentage between lot with gliclazide (lot 5) and lot with
glucomannan (at 6g/kg) and lot with hydrolysed glucomannan
(at 6g/kg). This proves that hydrolysed glucomannan (at 6g/kg
body weight) is capable of boosting cellular glucose tolerance. At
the times 3 hours and 4 hours after taking the preparations at a
dose of 3g/kg, the blood glucose reduction percentage was lower
than that of the lot with a dose 6g/kg of original glucomannan.
This difference is statistically significant, which proves that the
stimulation of glrsucose tolerence of hydrolysed glucomannan
at the dose of 3g/kg is ineffective. 3 hours and 4 hours after
taking the preparations, the blood glucose reduction of the lot
with hydrolyzed glucomannan is greater than that of the lot with
original glucomannan.


This difference is statistically significant with P<0,05. This
proves that the hydrolyzed product can stimulate the glucose
tolerance better than the original glucomannan. There are two
possible explanations: stimulation of glucose tolerance occurs
in brain, liver and red blood cells (cells that can receive glucose
without requiring insulin); or stimulation of insulin secretion,
increased insulin sensitivity of the preparations to target tissues
results in glucose tolerance of the target cells (hepatocytes,
muscle and adipose tissues, etc.). Whichever mechanism, this is
significant in the blood glucose reduction treatment for patients
with diabetes.
Conclusion
We have prepared low molecular weight glucomannan from
the bulbs of A. Konjac K Korch in Vietnam and demonstrated
the structure of the obtained product. The hydrolyzed product
has molecular weight of less than 1748,4Da and degree of
acetylation lower than the original glucomannan. The hydrolyzed
glucomannan at the dose of 6g/kg is more effective in reducing
blood glucomannan in mouse models that were made to raise
the blood glucose levels exogenously by oral administration, as
compared with the unhydrolyzed original glucomannan.
For more articles in Academic Journal of Polymer
Science please click on:
https://juniperpublishers.com/ajop/index.php
https://juniperpublishers.com/ajop/index.php


Comments
Post a Comment