The Making Process of Go/CT/PTFE Flat Sliding Plate of High-Speed Railway Bridge Spherical Bearings-Juniper Publishers
Authored
by Shou-ren Wang
Abstract
According to the rapid development of high-speed
railway, the importance of spherical bridge bearings has attracted lots
of attention as an essential connected part between bridge and pillar
[1,2]. As you know, high-speed railway spherical bearings consist of
upper bearings plate, spherical plate, under plate, flat stainless-steel
plate, flat sliding plate, spherical stainless steel plate, spherical
sliding plate, sealing ring, anchor bolt, dustproof shield [3,4]. Flat
sliding plate is an indispensable part of spherical bearings since the
displacement ability of bearings is determined by the sliding behavior
between flat stainless-steel plate and flat sliding plate.
Keywords: Spherical bridge; Steel plate; Sealing ring; Cold pressingMini Review
Now the flat plate is made of PTFE, which is
categorized as a chemical polymer and usually called “the king of
plastic”. As PTFE has a great ability of friction and wear, it has been
used widely. However, PTFE behave badly in creep deformation resistance
unless adding to original PTFE extra material which could improve the
performance to against creep deformation. One of the well-known extra
adding materials is GO [5,6]. GO is a kind of two-dimension nanometer
material with hive-like flat thin film, which is made of sp2 and found
in 2004. Although GO is as thick as one carbon atom, it has high level
yield strength and stiffness, great lubricant performance and excellent
wear-resistance attribute, and it means that GO could reduce friction
coefficient if it mixes with PTFE [7,8]. Another adding material called
CF which also has high level yield strength and elasticity
and could be added to PTFE to improve the wear resistance of material.
But, both GO and CF show low compatibility with PTFE as adding material
and many scholars and experts have
focused on this phenomenon. In this paper, it shows a new kind of making
process of Go/CF/PTFE flat sliding plate of high-speed railway bridge
spherical bearings by KH-550
Weighing Material and Mixing Material
The experimental material is weighed by electronic
universal analytical balance and then placed in grinding room of
planetary ball mill. The parameters are showed below.
Grinding time: 240 minutes, rotate rate: 180r/min, the ratio of ball to sample: 7:1
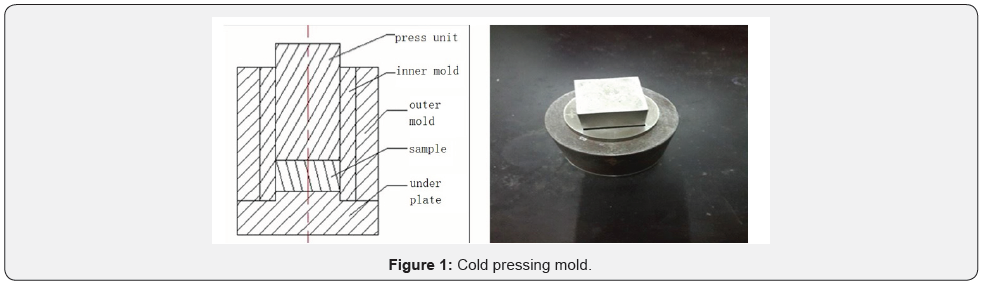
Cold Pressing
Put the sample into mold (Figure 1), and then
Universal hydraulic forming machine could press the sample. With
10MPa/min press velocity, the load pressure should increase gradually to
130MPa and stay for 10 minutes, to make sure the air among the sample
could be expelled entirely.
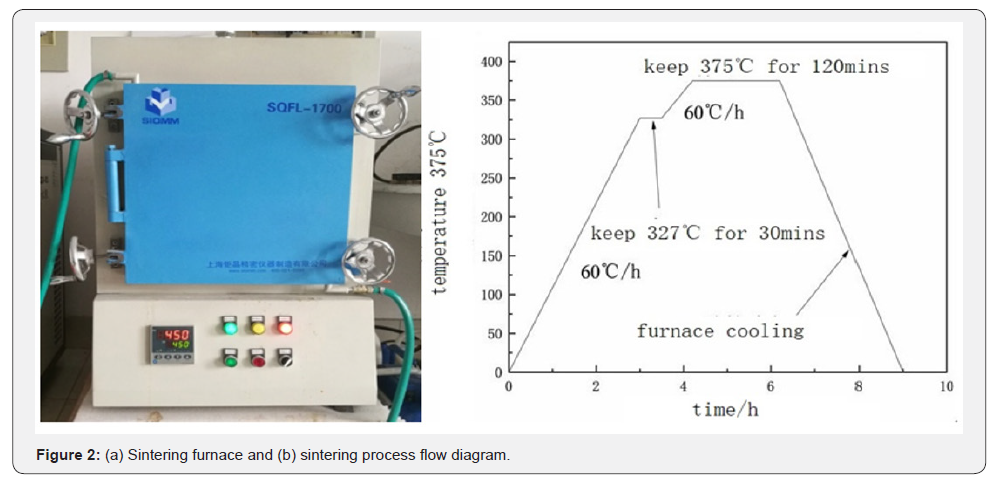
Sintering Solidification
After cold pressing process, the sample should be placed
into electric furnace for sintering. Figure 2 shows process flow
diagram. With 60 oC/h heating velocity, the sample should be
heated up to 327 oC, which is the melting point of the sample,
and then keep the temperature for 30 minutes. And then the
sample should be heated up to 375 oC and keep the temperature
for 2 hours. After furnace cooling process, the sample could be
considered well-prepared [9].
Microstructure Analysis
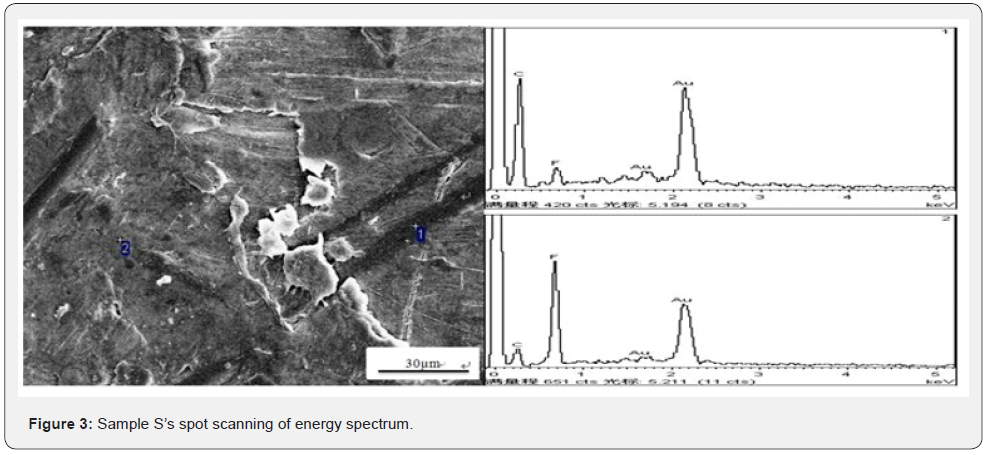
After making process of flat sliding plate, microstructure
analysis could be completed. Figure 3 shows sample S’s spot
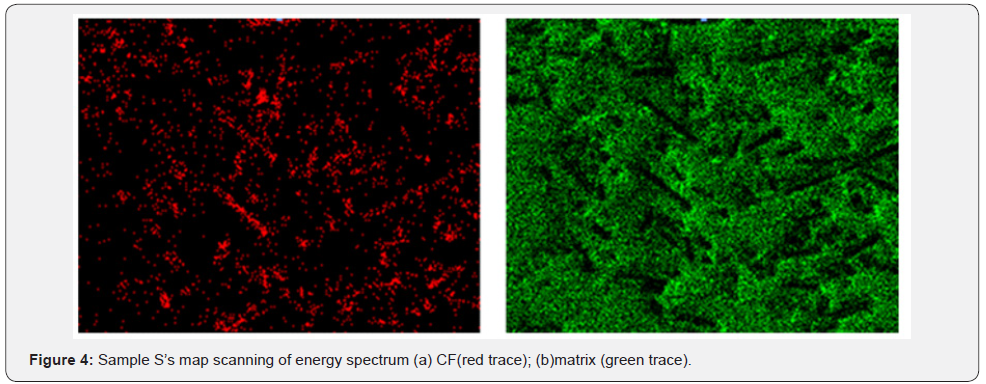
scanning of energy spectrum and Figure 4 shows sample S’s map
scanning of energy spectrum. In Figure 3, area 1 shows trace of
black strip, which is CF, and area 2 shows matrix material. Figure
4 also shows that CF has been distributed evenly in the matrix
material, and it means than CF has relatively good compatibility
and it could improve some kinds of strength property of sliding
plate sample [10]. Figure 5 shows the impact section microstructure
of composite sample. We can conclude that the
interface issue was not good from area 1 in Figure 5.

CF was extracted out from the material when it was
impacted. The combination between CF and matrix would turn
to be loose. Maybe it was caused by the incomplete disposition
by silane coupling agent, or the silane coupling agent disposition
couldn’t improve the interface issue between CF and PTFE.
The tight combination between CF and matrix which is shown
on area 3 in Figure 5, which proved that the interface issue
was solved seemingly. What is shown on area 2 in Figure 5 is
that the mid area of CF has been broken, which proved that CF
could strengthen the matrix. Area 4 in Figure 5 has shown the
gaps in composite material sample. Maybe it was caused by
the fast compressing rate of cold-press molding, or the liquid
evaporation during sintering process which was attributed to
the halfway drying of sample.
Conclusion
Bearings’ sliding plate sample could be made by cooling
press process and sintering solidification successfully, and since
CF could be distributed evenly among matrix, it illustrates that
CF could reduce wear and friction for material.
For more
details Journal of Polymer Science please
click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/ajop/index.php
To read more…Full Text in Juniper Publishers click on https://juniperpublishers.com/ajop/AJOP.MS.ID.555566.php


Comments
Post a Comment